Similar
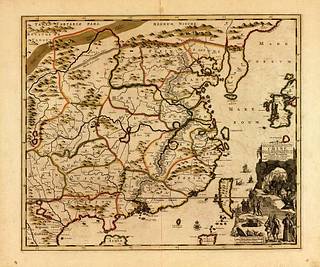
Carte exacte de toutes les provinces, villes, bourgs, villages et rivières du vaste et puissant empire de la Chine : faite par les ambassadeurs hollandois dans leur voyage de Batavia à Peking /
Summary
Relief shown pictorially.
Available also through the Library of Congress Web site as a raster image.
Includes ill.
LC copy annotated in ink on verso: 95.
Vault
Geoctroyeerde Westindische Compagnie, or Dutch West India Company, was a chartered company (known as the "WIC") of Dutch merchants. Among its founding fathers was Willem Usselincx (1567–1647). On June 3, 1621, it was granted a trade monopoly in the West Indies (meaning the Caribbean) by the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands and given jurisdiction over the Atlantic slave trade, Brazil, the Caribbean, and North America. The intended purpose of the charter was to eliminate competition, particularly Spanish or Portuguese, between the various trading posts established by the merchants. The company became instrumental in the Dutch colonization of the Americas. Some historians date the origins of the firm to the 1500s with arrivals of colonial settlers in what is now called New York long before the English at Jamestown, Virginia. The WIC was organized similarly to the Dutch East India Company (Dutch: Vereenigde Oost-Indische Compagnie, abbreviated as VOC). Like the VOC, the WIC company had five offices, called chambers (kamers), in Amsterdam, Rotterdam, Hoorn, Middelburg and Groningen, of which the chambers in Amsterdam and Middelburg contributed most to the company. The board consisted of 19 members, known as the Heeren XIX (the Lords Nineteen). The company was initially relatively successful; in the 1620s and 1630s, many trade posts and colonies were established. The largest success for the WIC in its history was the seizure of the Spanish silver fleet, which carried silver from Spanish colonies to Spain, by Piet Heyn in 1628; privateering was at first the most profitable activity. In 1629 the WIC gave permission to a number of investors in New Netherlands, which included New Amsterdam, covered parts of present-day New York, Connecticut, Delaware, and New Jersey. The settlers had little success with populating the colony of New Netherland, and to defend themselves against local Indians. The main focus of the WIC now went to Brazil and in 1630 the West India Company conquered a part of Brazil. Due to the Peace of Westphalia the hijacking of Spanish ships was no longer allowed. Merchants from Amsterdam and Zeeland decided to work with marine and merchants from Hamburg, Glückstadt (then Danish), England and other countries. In 1663 and 1664 the WIC sold more enslaved Africans than the Portuguese and English together. The first West India Company suffered a long agony and ended in 1674. The Collection includes Dutch maritime prints of the time period.
Ancient Maps from the Library of Congress. 13th -18th Century Maps.
In the 17th century, maps took a huge leap forward. Mathematical and astronomical knowledge necessary to make accurate measurements had evolved. English mathematicians had perfected triangulation: navigation and surveying by right-angled triangles. Triangulation allowed navigators to set accurate courses and produced accurate land surveys. Seamen learned to correct their compasses for declination and had determined the existence of annual compass variation. Latitude determination was greatly improved with the John Davis quadrant. The measurement of distance sailed at sea was improved by another English invention, the common log. Longitudinal distance between Europe and Québec was determined by solar and lunar eclipses by the Jesuit Bressani in the 1640s and by Jean Deshayes in 1686. With accurate surveys in Europe, the grid of the modern map began to take shape.
Tags
Date
Contributors
Source
Copyright info








![Carte historique et geographique des Royaumes D'Espagne et de Portugal divises selon leurs royaumes et provinces Nº 34[ [Material cartográfico] : avec privilege de noseigneurs les Etats de Hollande de West Frise Carte historique et geographique des Royaumes D'Espagne et de Portugal divises selon leurs royaumes et provinces Nº 34[ [Material cartográfico] : avec privilege de noseigneurs les Etats de Hollande de West Frise](https://cache.getarchive.net/Prod/thumb/cdn8/L3Bob3RvLzE3MzkvMTIvMzEvY2FydGUtaGlzdG9yaXF1ZS1ldC1nZW9ncmFwaGlxdWUtZGVzLXJveWF1bWVzLWRlc3BhZ25lLWV0LWRlLXBvcnR1Z2FsLWRpdmlzZXMtOWNiMDFkLTY0MC5qcGc%3D/40/33/jpg)


![A Map of the Kingdom of Poland and of the Grand Dutchy of Lithuania with their Dismembered Provinces and the Kingdom of Prussia [Mapa] A Map of the Kingdom of Poland and of the Grand Dutchy of Lithuania with their Dismembered Provinces and the Kingdom of Prussia [Mapa]](https://cache.getarchive.net/Prod/thumb/cdn8/L3Bob3RvLzE3OTIvMTIvMzEvYS1tYXAtb2YtdGhlLWtpbmdkb20tb2YtcG9sYW5kLWFuZC1vZi10aGUtZ3JhbmQtZHV0Y2h5LW9mLWxpdGh1YW5pYS13aXRoLXRoZWlyLTBhYjQzYy02NDAuanBn/40/33/jpg)


















































