Similar
Röntgen rays and electro-therapeutics - with chapters on radium and phototherapy (1910) (14571606499)
Summary
Identifier: rntgenrayselectr00kass (find matches)
Title: Röntgen rays and electro-therapeutics : with chapters on radium and phototherapy
Year: 1910 (1910s)
Authors: Kassabian, Mihran Krikor, 1870-1910
Subjects: Electrotherapeutics X-rays Phototherapy Radiology Radiotherapy
Publisher: Philadelphia & London : J.B. Lippincott Company
Contributing Library: Francis A. Countway Library of Medicine
Digitizing Sponsor: Open Knowledge Commons and Harvard Medical School
Text Appearing Before Image:
c acid, bismuth, iodoform,etc. I would urge that all lesions be covered with several layers of gauzewhile treatment is in progress. I. Apparatus and Method of Treatment. The a)3paratus necessary for intelligent and effective treatment ispractically the same as that employed for skiagraphic purposes. Thecurrent for exciting a tube is generated by a static machine, an inductioncoil of the Euhmkorff type, or a Tesla high-frequency apparatus. Someoperators prefer the static machine, believing that it does not produce adermatitis, but this has been proved a fallacy. Eegarding the size of thecoil for therapeutic purposes, one that is of seven or eight inch (18 to 20cm.) spark producing power will suf&ce. When using a coil for therapeutic purposes, the frequency of pro-longed exposures, often required, is liable to injure the insulation of thecoil. It is considered advisable to switch off the current and allow thecoil and the tube to cool every ten or fifteen minutes, during prolonged420
Text Appearing After Image:
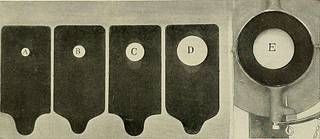
1.5 Fig. 210A.—Diameter of Diaphragms.—^Because of the immobilization of the part and its powerof cutting the secondary rays, I have within the past year resorted in certain special cases to the com-pression diaphragm, although heretofore I was not one of its advocates. The following are thedifferent distances for X-ray radiographic work, and also for therapy, taking the different sizes ofdiaphragms as here photographed in alphabetical order : For Roxtgen Therapy.in.A Lead Diaphragm areaB C D E The distance of the surface of the tube from the part being(1-5 cm.) using a G in. (1.5 cm.) diameter-tube, and for larger tubes the area covered should be reducedin proportion to the distance of the anode from the diaphragm. Eontgexographic Exposures. in. cm. in. cm. D Lead Diaphragm area 8 x 10, plate 20 x 25, distance 26 to 28 65 to 70E 11x14, 28x35, 24 60 E ■ •■ 14x17, 35x42, 18 to 20 45 to 50 Always use lead diaphragm D for 8 in. x 10 in. (20 x 25 cm.), or smaller plates, or when
Tags
Date
Source
Copyright info





















