Similar
Röntgen rays and electro-therapeutics - with chapters on radium and phototherapy (1910) (14754917021)
Summary
Identifier: rntgenrayselectr00kass (find matches)
Title: Röntgen rays and electro-therapeutics : with chapters on radium and phototherapy
Year: 1910 (1910s)
Authors: Kassabian, Mihran Krikor, 1870-1910
Subjects: Electrotherapeutics X-rays Phototherapy Radiology Radiotherapy
Publisher: Philadelphia & London : J.B. Lippincott Company
Contributing Library: Francis A. Countway Library of Medicine
Digitizing Sponsor: Open Knowledge Commons and Harvard Medical School
Text Appearing Before Image:
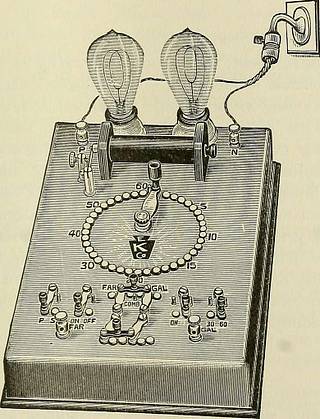
e started so as to form a circuitbetween the coil and cell or battery. The current produced by a fa-radic equipment is alternating in character, as may be readily demon-strated when applied to the tissues. Instead of a current from a cell,advantage is often taken of a direct 110-current, as is well illustrated inFig. 29. INDUCED CURRENTS. 45 Interrupter or Eheotome. The interrupter wliicli forms an essential part of the battery is thevibrating spring hammer of Neef. Many authorities condemn this formof rheotome, and recommend one which has double the ordinary springlength, both ends being attached to posts, to one of which is connected atension-screw for regulating the rate of vibrations. The armature isattached to the middle of the brass spring and platinum plate for contactnear the fixed post. Besides regulating the frequency and amplitude ofthe vibrations by the tension-screw, we regulate them also with the set-screw carrying the platinum contact point. This device gives easily the
Text Appearing After Image:
Fig. 29.—Galvanic and faradic lamp controller. rate of vibration suitable for muscular contraction, and this is from 1 toabout 3000 per minute. Vibrations above 3000 per minute are sedative.The highest stimulation is from 3000 to 4000 interruptions per minute. Method of Application. This method of electrization consists in placing one pole, generallythe negative, at the feet or coccyx, while the other is applied to any partof the surface. The current may be applied (stabile) stationary or(labile) moving ; it may be increased or decreased in intensity accordingto the desire of the operator. The person applying it should have someexperience, so that the very best results may be obtained. 46 ELECTEO-THERAPEUTICS. Localized Faradization. Localized faradization, as termed by Duchenne, or, more correctly,polar faradization, in contradistinction to the polar and bipolar methodof galvanization, is applied in precisely the same manner as is the galvaniccurrent. This localized or polar method
Tags
Date
Source
Copyright info





















