Similar
European foulbrood BHL41863898
Summary
Plate VII
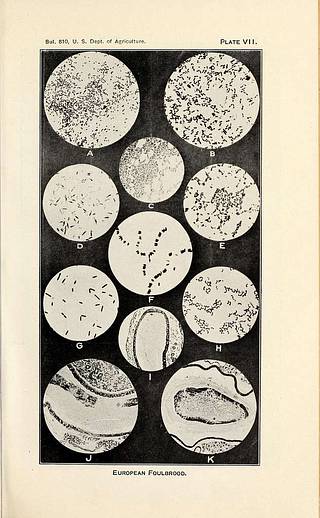
Photomicrographs illustrating the more commonly encountered bacteria in European foulbrood.
A. — Bacillus pluton: A smear from the stomach of a larva sick with European foulbrood. Note the paired forms and short chains. These forms are numerous in a recent infection, suggesting the organism in the process of multiplication. The lancet-shaped form is by far the predominant one in all later stages of the disease. X 1000.
B. — Bacillus pluton: A smear from a larva quite recently infected. The multiplying paired forms are at this stage present almost exclusively. X 1000.
C. — Bacterium eurydice: Stained preparation from a pure culture on the surface of agar. X 1000.
D. — Bacillus alvei: Stained preparation showing spores and spore formation. X 800.
E. — Streptococcus apis: Stained preparation from a pure culture. X 800.
F. — Bacillus alvei: The peculiar arrangement of the spores as sometimes seen. From a pure culture, the smear having been made by suspending the culture on the slide in normal salt solution. X 1000.
G. — Bacillus orpheus: Stained preparation made from a pure culture only a few hours old. Grown on the surface of agar. X 1000.
H. — Bacillus orpheus: Stained preparation showing spore formation. Note the stained portion along one side and about both ends of the spore. The stage is soon reached in a culture at incubator temperature. At room temperature it remains in this stage for a considerable period. X 800.
I. — Longisection of a young larva showing early infection in European foulbrood. The bacterial growth is seen as a narrow black area just within the peritrophic membrane on one side of the food mass.
J. — Longisection of larva sick of European foulbrood. showing a later stage of infection than that present in I. The dark area in the food mass shows the bacterial growth. Note that the growth mass does not extend beyond the peritrophic membrane and that it does not extend uniformly along this membrane and throughout the food mass.
K. — Transverse section of larva about the time of its death from European foulbrood infection. Note the bacterial mass along the peritrophic membrane and extending from the membrane into the food mass. As seen within the living larva this bacterial mass in the sick larva is practically white, but is more or less yellowish white when present with larval food material. The gelatinous-like envelope outside the peritrophic membrane and inside the stomach epithelium in healthy larvae thins out as the disease advances.
Tags
Date
Source
Copyright info



















