Similar
Chois from BL Arundel 93, f. 150 - Public domain old map
Zusammenfassung
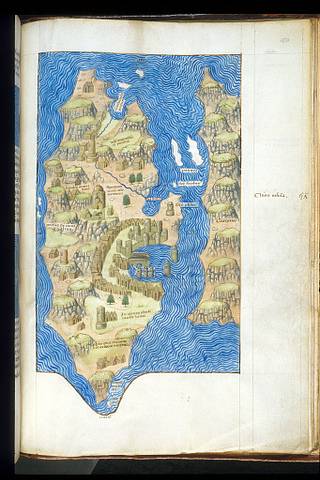
Miniature of a map of the island of Chios. Image taken from f. 150 of Liber insularum archipelagi. Written in Latin.
The Arundel Manuscript Collection was amassed by the Howard family, particularly Thomas Howard, the 2nd Earl of Arundel (1585-1646). Thomas Howard, the 2nd Earl of Arundel, who was a prominent figure during the early 17th century in England. Thomas Howard enjoyed a close relationship with King Charles I, and this connection allowed him to expand his collection. The king was granting him privileges to purchase manuscripts and books, and the collection grew in size and importance.
The English Civil War and the execution of King Charles I had a significant impact on Thomas Howard's life. During the war and the Commonwealth period, his collection faced threats of dispersion and destruction. Howard managed to protect many of his books and manuscripts by sending them abroad for safekeeping. After the restoration of the monarchy in 1660, the collection was returned to the Howard family.
Während des Mittelalters wurden die europäischen Karten von religiösen Ansichten dominiert. Alle Karten wurden natürlich von Hand gezeichnet und beleuchtet, was die Verbreitung der Karten extrem begrenzt machte. Die mittelalterliche Geographie teilte die Welt in drei schematische Teile: Asien, Europa und Afrika. Asien wurde oben als Geburtsort Christi und ursprünglicher Standort des Gartens Eden dargestellt. Eine T-O-Karte (orbis terrarum, Orbis oder Kreis der Länder; mit dem Buchstaben T innerhalb eines O), auch als Isidorsche Karte bekannt, ist eine Art frühe Weltkarte, die die physische Welt darstellt, wie sie zuerst vom Gelehrten Isidor von Sevilla im 7. Jahrhundert in seinem De Natura Rerum und später in seinen Etymologiae beschrieben wurde. In diesem Kartenformat wurde Jerusalem in der Mitte dargestellt, und der Osten orientierte sich in Richtung Kartenspitze. Das Design hatte große religiöse Bedeutung, wobei das "T" das zentrale christliche Symbol des Kreuzes darstellte und Jerusalem in den Mittelpunkt der Welt stellte. Das "T" trennte auch die Kontinente der bekannten Welt - Asien, Europa und Afrika - und das "O", das das gesamte Bild umgab, repräsentierte die mittelalterliche Idee einer Welt, die von Wasser umgeben war.
Tags
Datum
Quelle
Copyright-info
























