Similar
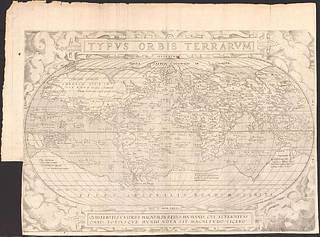
Typvs orbis terrarvm, Abraham Ortelius
Summary
Oval map within illustrated border, showing clouds.
Includes illustrations.
Appears to be an etched, probably unauthorized copy of an edition Ortelius's map, possibly made in Italy. This map copies the re-engraved clouds in lower left corner, which, according to Shirley, dates the map to 1579 or later. The word "occidens" on the left edge of the map reads bottom to top rather than top to bottom as in the original. On laid paper with a watermark of a bunch of grapes.
LC copy trimmed, with narrow right and bottom margins. Left margin also cut away in lower corner.
Available also through the Library of Congress Web site as a raster image.
The geography discoveries and the new printing techniques resulted in maps that can be cheaply produced. Since a globe remains the only accurate way of representing the spherical earth, and any flat representation resulted in distorted projection. In 1569, Mercator published a map of the world specifically intended as an aid to navigation. It used a projection now known by Mercator's name, though it has been used by few others before him, based on a system of latitude and longitude that dated back to Hipparchus. Mercator's projection greatly enlarged territories as they recede from the equator. The distortion of Mercator's projection is a benefit to navigators since Mercator achieves a matching scale for longitude and latitude in every section of the map. A compass course can be plotted at the same angle on any part of Mercator's map. As a result marine charts still use this projection. By the time of his death in 1595, Mercator has either published or prepared large engraved maps, designed for binding into volume form, of France, Germany, Italy, the Balkans, and the British Isles. Mercator's son issues the entire series under the title "Atlas": "Atlas sive Cosmographicae Meditationes." The name becomes the word for a volume of maps.
Tags
Date
Location
Source
Copyright info




















