Similar
Röntgen rays and electro-therapeutics - with chapters on radium and phototherapy (1910) (14757810482)
Summary
Identifier: rntgenrayselectr00kass (find matches)
Title: Röntgen rays and electro-therapeutics : with chapters on radium and phototherapy
Year: 1910 (1910s)
Authors: Kassabian, Mihran Krikor, 1870-1910
Subjects: Electrotherapeutics X-rays Phototherapy Radiology Radiotherapy
Publisher: Philadelphia & London : J.B. Lippincott Company
Contributing Library: Francis A. Countway Library of Medicine
Digitizing Sponsor: Open Knowledge Commons and Harvard Medical School
Text Appearing Before Image:
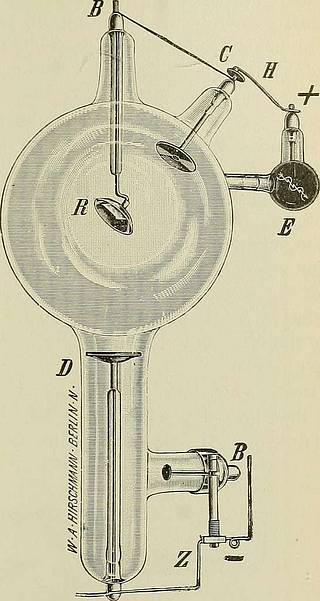
of the pelvis) U 10-11 cm.,for soft rays (diagrams of the haud) 5-7 cm., for treatment even less.The working of the • Miiller regulation may be observed by the sparkspassing between E andK. As soon as thisstops, the tube has the de-sired degree of vacuum andwill maintain the same au-iomaticalJy by an occasionalspark jumping over andreducing the vacuum, assoon as the latter shows atendency to rise. In casethe automatic way of lower-ing the vacuum should re-quire too much time, it canbe hastened by either ap-proaching the wire Eeven closer to K, orfinally connecting the nega-tive pole to the loop C.In this latter event specialcaution is recommended, astubes easily become toosoft and a hardening ismore difficult. Hardening a tube iseffected by changing thepositive pole from G toJ and removing thewdre E far off from K. AYhen the currentis now turned on, it willscatter atoms of the metalof the electrode J, thusreabsorbing part of the gasof the tube. This processrequires up to 5 minutes.
Text Appearing After Image:
Fig. 91.—Monopol tube. The vacuum may be alteredduring the process by the generation of air through thedisconnection of the movable conductor Z, or by the ab-sorption of air through the disconnection of the movableconductor H. The flexible wire Z is raised for someseconds by means of an isolated rod until a spark leaps overto the auxiliary cathode at B, by means of which air isgenerated and the resistance of the tube lowered. Tubes inwhich the degree of generation has become excessive aremodified by raising the movable conductor H as shown inthe sketch. Air is generated by the disconnection of theflexible conductor Z and the leaping over of sparks toB, and accordingly the degree of the vacuum in the tube16 lowered. Air is absorbed by disconnecting the flexibleconductor H, and the resistance of the tube is increased. according to the vacuum,and may have to be repeated. It is not advisable to change the vacuumof a tube too often. For different purposes different tubes should be em-plo
Tags
Date
Source
Copyright info




















