Similar
A manual of practical medical electricity - the Röntgen rays and Finsen light (1902) (14780544671)
Summary
Identifier: manualofpractica00turn (find matches)
Title: A manual of practical medical electricity : the Röntgen rays and Finsen light
Year: 1902 (1900s)
Authors: Turner, Dawson
Subjects: X-Rays Electrophysiology Electrosurgery Electric Stimulation Therapy Electrotherapeutics X-rays Electrophysiology Electrosurgery
Publisher: New York : William Wood & Company
Contributing Library: Francis A. Countway Library of Medicine
Digitizing Sponsor: Open Knowledge Commons and Harvard Medical School
Text Appearing Before Image:
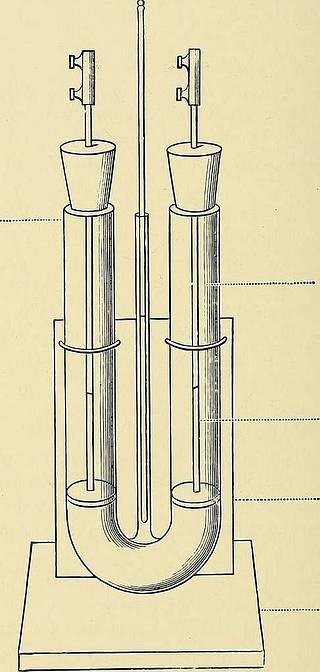
ternating currentsand a telephone, according to Kohlrauschs method, and ata temperature of 65° Fahrenheit. Fig. 100 is a view of theelectrolysis tube used. It would appear from the observations (some 500 innumber) that the specific resistance of a normal urineamounts to about forty-five ohms, and that it varies as arule inversely with the specific gravity. The latter is ameasure of the amount of solids in solution, and particu-larly of the urea. It might be supposed, then, that theresistance depends also mainly upon the amount of urea ;this, however, is not the case. Numerous experimentswere made with artificial solutions of urea, sodium chloride,phosphates, sugar in distilled water (see Table I., i, 3, 4), 13 194 A Manual of Practical Medical Electricity and from these it is clearly apparent that the electricalresistance depends almost wholly upon the salts, chlorides,phosphates, sulphates, etc., and that it is only when theseare absent, or diminished, that the influence of the urea
Text Appearing After Image:
Fig. ioo.—U Tube used for Measuring the ResistanceOF Liquids. Tnakes itself felt. The resistance is therefore a measure of the chemically active substances in a urine, of the salts (p. 172), and to a very much less degree of the inert urea. This gives us a simple and rapid method of estimating Electro-Diagnosis 195 the constitution of a urine as regards its salts, while thespecific gravity in the absence of sugar is a guide to itsurea. In a normal urine, as already stated, these go more orless inversely together ; given the specific gravity, the re-sistance can be estimated ; and given the resistance, thespecific gravity can be calculated. To the rule that the resistance varies inversely with thespecific gravity there are certain exceptions : these canbe arranged accordingly as they occur in acute or in chronicdiseases. Excluding acute infectious diseases and local surgicalaffections, the two most prominent exceptions are,amongst the former, acute croupous pneumonia ; amongstthe lat
Tags
Date
Source
Copyright info

























