Similar
A manual of practical medical electricity - the Röntgen rays and Finsen light (1902) (14803526923)
Summary
Identifier: manualofpractica00turn (find matches)
Title: A manual of practical medical electricity : the Röntgen rays and Finsen light
Year: 1902 (1900s)
Authors: Turner, Dawson
Subjects: X-Rays Electrophysiology Electrosurgery Electric Stimulation Therapy Electrotherapeutics X-rays Electrophysiology Electrosurgery
Publisher: New York : William Wood & Company
Contributing Library: Francis A. Countway Library of Medicine
Digitizing Sponsor: Open Knowledge Commons and Harvard Medical School
Text Appearing Before Image:
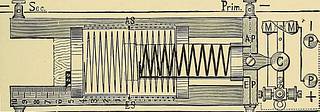
Faradic Electricity 117 position in which the latter may be (the distance from theprimary coil) may be accurately noted. A bundle of soft iron wires covered with an insulatingvarnish, and enclosed in a light case, which is graduated,can be placed within or withdrawn to any required degree,according to the graduations, from the primary coil. Thisforms an electro-magnet, which is more rapidly magnetiz-able and demagnetizable than a solid one would be,because the induction currents, which would be set incirculation in a solid rod, are partly eliminated. The primary coil is wound with a few turns of thickwire to diminish resistance and self-induction. The secondary coil is wound with very many turns of
Text Appearing After Image:
TSScc. Prim. J,+ Fig. 70.—Diagram of Induction Coil from Above. thin wire, which must be most carefully insulated fromeach other to prevent the high electromotive forceliberated from short-circuiting. The greater the numberof the coils, the greater the mutual induction and electro-motive force. The increased resistance may, therefore,be disregarded. To open and close the primary circuit with rapidity, amechanical arrangement, known as Neefs hammer, isemployed (Fig. 69). When a current is passed throughthe electro-magnet B, it attracts to it the movable arma-ture C, which at other times is kept in contact with theplatinum-faced screw A by the spring D. If the circuit be closed in such an arrangement, thecurrent, entering by the pillar E, will flow through the ii8 A Manual of Practical Medical Electricity armature C, and along screw A into the primary coil,returning round the electro-magnet B, which thereforebecomes magnetized, and attracts the armature C, break-ing its contact with A
Tags
Date
Source
Copyright info
























